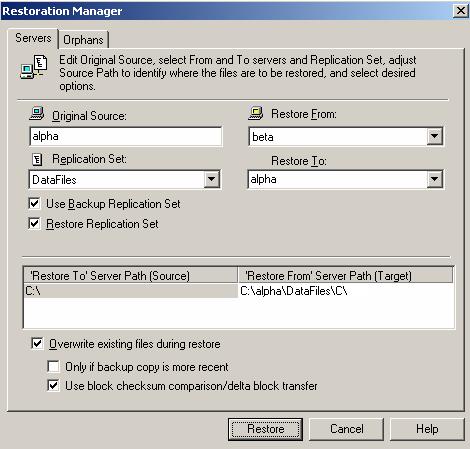
Failback before restoration can be a simpler process, but it may require additional downtime. The amount of downtime will depend on the amount of data to be restored. Users must be kept off of the source and target during this entire process.
| Note: |
If the target is a cluster, you will need to determine the active node and failback from that node. Then you will need to failback from each of the other nodes to synchronize all of the nodes of the cluster. |
| Note: |
The source must be online and Double-Take Availability must be running to ensure that the source post-failback script can be started. If the source has not completed its boot process, the command to start the script may be lost and the script will not be initiated. |

| Note: |
If your target is a cluster, you can specify just one node in the cluster and restore only from that node. If you need to have the cluster functionality (Microsoft failover from node to node) available during the restoration process, you will have to create a resource, like you did for your original connection, for the restoration process. See Protecting a standard cluster. Keep in mind when restoring, your target will function as your source, sending data to the target, which will be your original or new source. |
| Note: |
Restoring across a NAT router requires the ports to be the same as the original connection. If the ports have been modified (manually or reinstalled), you must set the port numbers to the same values as the last valid source/target connection. |
| Note: |
If you are using a database application, do not use the newer option unless you know for certain you need it. With database applications, it is critical that all files, not just some of them that might be newer, get mirrored. |
| Note: |
If your target is a cluster, take the Double-Take Source Connection resource offline to disconnect the connection. During the restoration, only the data is restored back to the source. Shares are not created on the source during the restoration. Shares that were created on the target during failover will need to be created manually on the source. |