Open topic with navigation
Protecting a SharePoint server
The SharePoint databases will be protected by default and the Application Manager can be used to extend the target web front-end into the source SharePoint configuration.
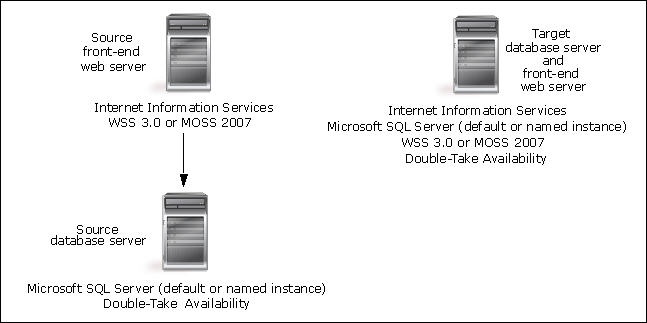
To configure protection for your SharePoint servers using Application Manager, you will complete the following steps:
- Configure each source as a Windows member server.
- Install Microsoft SQL Server on each source that will be used as a back-end server.
|
Note:
|
For SQL Server 2000, Microsoft recommends that all service packs be installed independently for each source and target instance. This ensures that operating system files and registry entries are applied appropriately.
|
- Install and configure Windows SharePoint Services (WSS 3.0) or Microsoft Office SharePoint Server (MOSS 2007) on each source that will be used as a front-end server, according to Microsoft guidelines.
- Configure each Windows 2003 target as a member server in the same Active Directory domain or trusted domain environment as the source.
- Install SQL on the target, verifying that the locations for the SQL installation and the location of the data and log files for the target are the same as the source. Apply the same SQL service packs or patches as were installed on the source. Use the default installation options for SQL with the following considerations:
- The target must be a unique installation (that is, two separate SQL servers must be available for a protection pair)
- Logical drive mapping must be the same on the source and target and must assigned prior to running the Application Manager.
|
Note:
|
For SQL Server 2000, Microsoft recommends that all service packs be installed independently for each source and target instance. This ensures that operating system files and registry entries are applied appropriately.
|
- Install WSS 3.0 or MOSS 2007 on the target server, but DO NOT configure it if you want to use Application Manager to extend the target into the Web Farm.
- Install Double-Take Availability on the source and target SQL servers using the installation defaults.
- Launch the SharePoint Server protection workflow.
- Select a domain.
- Select the SharePoint front-end.
- Select source and target servers.
- (Optional) Configure protection settings.
- Validate the configuration.
To protect your SharePoint server, you will complete the following steps:
- Enable protection.
- Monitor protection.
In the event of a failure, you will need to perform some additional tasks. These tasks are described in Failover, failback, and restoration.
Next step: Launch the SharePoint protection workflow

