By default, all of the SharePoint program and data files (except the \binn directory) are selected for replication to the target SharePoint server. This will allow the clients to access your production SharePoint server data and functionality on the target in the event of a failure.
The source and target servers must both have the exact same version of SharePoint (major and minor versions) as well as similar logical drive structures (the target must have at least the same logical drives as the source where SharePoint program and data files are stored).
|
Note:
|
- If you are using a SQL server named instance for a back-end database server in your SharePoint setup, both the source and target SQL servers must have named instances with the exact same name and logical drive structure as the source SQL server installed prior to configuring protection.
- To enable the ability to add or remove SharePoint instances, you can launch Application Manager through the command line using the /sharepoint /advanced option (dtam /sharepoint /advanced). With this option enabled, a dialog box will appear when you select Configure Protection.
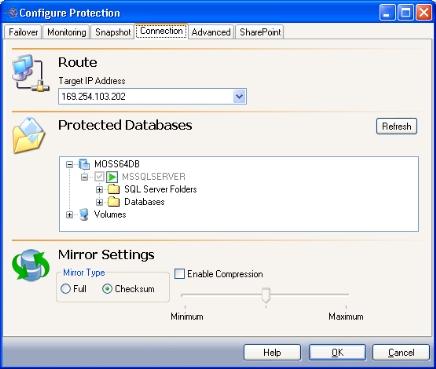
- If you need to reduce the amount of mirroring and replication traffic, you may choose to deselect the tempdb database if it is not necessary.
|
You can also select non-application specific data under the Volumes folder.
|
Note:
|
If Override Generated Rules is selected on the Advanced tab, this control will be disabled.
|
To refresh the tree view to show new source directories or files that may have been added or removed, select the logical node, then click the Refresh button. If a node in the volumes branch is selected, then the items under that node will be refreshed.