If you have not done so already, launch the Protecting a SQL Server workflow.
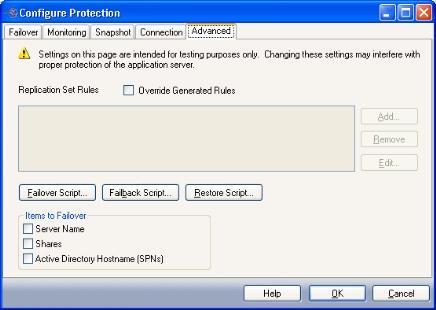
The Advanced tab includes advanced configuration options.
|
|
The following topics explain how to configure the options on the Advanced tab:
A replication set defines what directories/files are to be protected by Double-Take Availability. By default, Application Manager selects all of the necessary directories/files to protect SQL based on your source server configuration. These include the SQL application data and transaction logs, tempdb files, and SQL error logs. By default, the Application Manager-generated replication set will be named sqldag01_<source server name>_<target server name>.
You should only modify the replication set rules if there are additional directories/files specific to your configuration that must also be protected with SQL. Modifying the default configuration for replication set rules may affect whether data can be successfully replicated. Do not modify the replication set unless you are very familiar with Double-Take Availability and SQL.
To change the replication set rules:
|
Note: |
When this box is selected, the Protected Databases control on the Connection tab will be disabled. For more information, see Protected databases. |
|
|
|
Note: |
You will need to manually verify that the rule path is correct since the Application Manager does not validate rule paths. |
|
Note: |
Removing rules that were automatically added by Application Manager could impact the success of failover. Any changes to rules should be thoroughly tested. |
Scripts are executed at different points during the failover/failback process to perform the actions necessary to make SQL available on the appropriate server. Scripts perform steps such as starting/stopping services, attaching/detaching databases in database-only protection mode, and modifying DNS entries on the DNS server to point users to the appropriate server.
Editing scripts is an advanced feature. Do not edit scripts unless you fully understand what each command is doing.
Scripts are automatically generated by Application Manager during configuration. The scripts are copied to the Double-Take Availability installation directory on the specified server using the administrative share for that server’s drive.
|
Script |
File name |
Description |
|---|---|---|
|
Failover |
post_failover_sql.txt |
A post-failover script is executed after the core failover processes have completed on the target server. The primary functions of the post-failover script are to start the services on the target and to modify DNS and Active Directory entries as necessary. |
|
Failback |
pre_failback_sql.txt |
A pre-failback script is executed before failback processing occurs on the target server. The primary functions of this script are to stop services on the target and to move DNS and Active Directory entries as necessary. |
|
Restore |
post_restore_sql.txt |
A post-restore script is not executed automatically, though it is provided on the source to perform actions that are generally required after data has been restored from the target to source after a failover/failback. The primary function of this script is to restart services on the source server. |
By default, Application Manager generates all the required scripts for you automatically based on your system configuration. You can also edit the scripts to add, modify, or delete specific commands. To edit a script:
Any change you make to the script in the editor will be copied to the appropriate server when configuration changes are accepted, thus overwriting any changes that have been made outside the Application Manager.
The scripts can be overwritten by certain operations during setup. For example, any changes to configuration options done in the Application Manager will overwrite previous script changes. If you want to make permanent changes to a script, you must modify the appropriate .txt file within the Application Manager installation directory. If there is more than one client machine that will be configuring failover, the change must be made to all the appropriate .txt files.
Before running Application Manager multiple times (for example, when re-enabling protection after a failover/failback), save a copy of your post-restore and pre-failback batch files. After Application Manager executes, replace the default script file(s) with the customized file(s) that you saved.
Select the items to failover.
| Note: | After failing over the server name in a SQL 2008/Windows 2008 workgroup, you can't connect to any SQL instance on the target. Do not failover the server name on SQL 2008/Windows 2008. |
|
Note: |
If you are using Active Directory, you should enable this option. Otherwise, you may experience problems with failover. |
The following options allow you to control what functions Application Manager will perform during configuration. By default, Application Manager performs all of these functions. Individual functions should only be disabled for testing or debugging purposes.
|
Note: |
These options are only available when you launch Application Manager using the command line /sql /advanced option (dtam /sql /advanced). |
|
|
Next step: Save configuration settings
 Replication set rules
Replication set rules