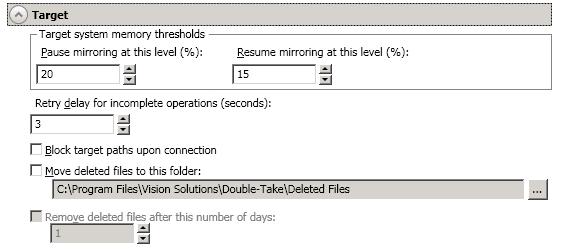
These properties are specific to the target server role.

Block target paths on connection—You can block writing to the replica source data located on the target. This keeps the data from being changed outside of Double-Take processing.
Do not block your target paths if you are protecting an entire server because system state data will not be able to be written to the target.
Be careful blocking target paths if you will be using Double-Take snapshots. You will have to unblock the paths before you can failover to a snapshot. Additionally, be careful when blocking target paths with backup software running on the target. You will need to unblock the paths to allow backup software to take snapshots or update archive bits.
Move deleted files to this folder—This option allows you to save files that have been deleted, by moving them to a different location on the target. When a file deletion is replicated to the target, instead of the file being deleted from the target, the file is moved to the specified location. This allows for easy recovery of those files, if needed. If you enable this option, specify where you want to store the deleted files.
If you are moving deleted files on the target and you have orphan files configured for removal (which is the default setting for most job types), do not move the deleted files to a location inside the replica data on the target. The deleted files that are moved will then be deleted by the orphan file functionality.
Remove deleted files after this number of days—If you are moving deleted files, you can specify a length of time, in days, to maintain the moved files. A moved file that is older than the specified number of days will be deleted. Double-Take checks for moved files that should be deleted once daily at 8 PM. Only the date, not the time, of the file is considered when moved files are deleted. For example, if you specify to delete moved files after 30 days, any file that is 31 days old will be deleted. Because the criteria is based on days and not time, a file that will be deleted could have been moved anytime between 12:01 AM and 11:59 PM 31 days ago.
If deleted files are moved for long enough, the potential exists for the target to run out of space. In that case, you can manually delete files from the target move location to free space.
Do not include the Recycler directory in your job if you are moving deleted files. If the Recycler directory is included, Double-Take will see an incoming file deletion as a move operation to the Recycle Bin and the file will not be moved as indicated in the move deleted files setting.
Alternate data streams that are deleted on the source will not be moved on the target.
Encrypted files that are deleted on the source will only be moved on the target if the move location is on the same volume as the copy of the source data on the target.
Compressed and sparse files that are deleted on the source will be moved on the target, although the compression and sparse flags will only be retained on the target if the move location is on the same volume as the copy of the source data on the target.