

|
When a failover condition has been met, failover will be triggered automatically if you configured automatic failover when establishing protection. If you configured manual intervention before failover, you can use the Application Manager to initiate failover for application workloads configured for DNS failover.
In a clustered environment where the source suddenly becomes unavailable (for example, it crashes) and the Application Manager is open, it may appear to be unresponsive for up to 30 minutes before the failover process continues. The Application Manager is waiting on a Microsoft cluster file to respond. To reduce the amount of time before failover can continue, close and re-open the Application Manager.
If you are protecting a file server, failover is only available if the source is offline, in order to prevent name conflicts on the network.
In the Application Manager, make sure your source target pair is selected and then on the Monitor tab, click Failover.
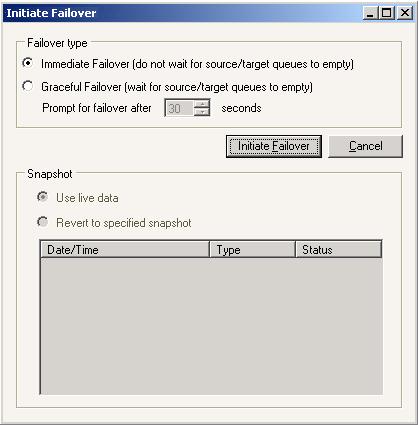
Specify if you want to perform an immediate or graceful failover. An immediate failover begins immediately without waiting for the data queues on the source and target to empty. A graceful failover waits until the queues are emptied before continuing. If you select the graceful failover, specify how often you want the failover prompt to continue asking for failover while there is still data in the queues.
If you are protecting an Exchange virtual server in a cluster environment, you should use the graceful failover option so that the source cluster resources are taken offline gracefully.
If you are protecting a file server, the graceful failover option is not available.
The following notes apply to Exchange protection.
Users using Outlook or Outlook Web Access to receive e-mail can connect after the changes have propagated through your environment. Users that had Outlook open during failover will need to restart the Outlook client (excluding Outlook Web Access clients on a LAN). Additionally, those users using Outlook Web Access or Outlook 2007 may see a security alert because the security certificate has the source server name but Exchange is now on the target. Click Allow or OK to dismiss the alert.
You will not be able to log in to the domain from the source Exchange server after failover because the target has assumed the source server's host Service Principal Name so that Outlook Web Access can use the source name. If you need to log in to the domain and Outlook Web Access is not needed, contact technical support for a workaround.
If you SMTP gateway is configured to send e-mail to a specific IP address that address is not failed over to the target, you will need to update the IP address after failover.
Mail stores or storage groups created after a failover will not be failed back.
The following notes apply to SQL protection.
After failover, linked databases in the SQL instance will be unavailable until the service master key is updated. You will need to run the command "alter service master key force regenerate" against the SQL target server to reset the service master key and then remove and re-add the linked servers into the target SQL instance.
After failover with a snapshot of a SQL database-only server, the SQL services on the target server are stopped and the databases are not mounted. You will need to manually start the MSSQLServer service for each instance on the target server and then manually attach the databases.
After failing over SQL 2008, Rich Internet Applications created using ADO.net 2 may not connect.
After failing over SQL 2008, you may not be able to take the SQL database offline. If this occurs, stop and restart the SQL Server Management Studio application, and then you can take the database offline.
After failing over in a SQL workgroup, you will not be able to connect to the source server instance of SQL. You can work around this issue by creating an alias on the target with the source server’s name.