Open topic with navigation
Failing over using the Full-Server Failover Manager
When a failover condition is met, you will want to start failover. Additionally, you can start it without a failover condition, as long as protection is enabled. For example, you may want to force failover when upgrading to a better source server.
- To start failover, click Failover.
-
If Double-Take Availability determines there is a possibility that the data on the target is incomplete, you will be warned before failover begins. If you proceed with failover, the state of the source will be unknown until failover is complete. The best case scenario would be a missing data file, while the worst case scenario would be missing system state data that causes the server to be unusable or unbootable. Select your failover options.
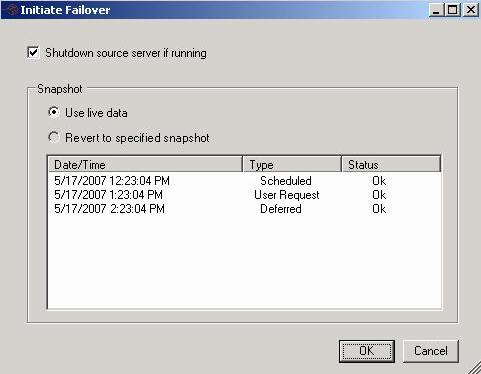
- Shutdown source server if running—If the source is still running, Full-Server Failover Manager can stop it. Although, if Full-Server Failover Manager cannot communicate with the source, the shutdown command will fail. This option prevents network conflicts in those cases where the source and target are still both running and communicating, such as a forced failover.
- Use live data—Select this option to use the data on the target at the time of failover.
- Revert to specified snapshot—Select this option, and then select a snapshot. The data on the target will be reverted to the selected snapshot. This option will not be available if there are no snapshots on the target or if the target does not support snapshots. To help you understand what snapshots are available, use the Type and Status columns. The Status indicates the state of the connection between the source and target at the time the snapshot was taken. The Type indicates the kind of snapshot.
- Scheduled—This snapshot was taken as part of a periodic snapshot.
- Deferred—This snapshot was taken as part of a periodic snapshot, although it did not occur at the specified interval because the connection between the source and target was not in a good state.
- User Request—This snapshot was taken manually by a user.
- Click OK to initiate failover. Monitor the failover percentage as shown in the Protection Status. At the end of failover, the target will be rebooted automatically. After the reboot, the target will no longer exist, since it will become the source.
Note: Because the Windows product activation is dependent on hardware, you may need to reactivate your Windows registration after failover. In most cases when you are using Windows 2003, you can follow the on-screen prompts to complete the reactivation. However, when you are using Windows 2008, the reactivation depends on your licensing type. If a Windows 2008 target comes online after failover with an activation failure, use the steps appropriate for your license type.
- Retail licensing—Retail licensing allows the activation of a single operating system installation.
- Open the System applet in Windows Control Panel.
- Under Windows activation at the bottom of the page, click Change product key.
- Enter your retail license key. You may need access to the Internet or to call Microsoft to complete the activation.
- MAK volume licensing—Multiple Activation Key (MAK) licensing allows the activation of multiple operating system installations using the same activation key.
- View or download the Microsoft Volume Activation Deployment Guide from the Microsoft web site.
- Using an administrative user account, open a command prompt and follow the instructions from the deployment guide to activate MAK clients. Multiple reboots may be necessary before you can access a command prompt. You may need access to the Internet or to call Microsoft to complete the activation.
- KMS volume licensing—Key Management Service (KMS) licensing allows IT professionals to complete activations on their local network without contacting Microsoft.
- View or download the Microsoft Volume Activation Deployment Guide from the Microsoft web site.
- Using an administrative user account, open a command prompt and follow the instructions from the deployment guide to convert a MAK activation client to a KMS client. Multiple reboots may be necessary before you can access a command prompt.
 Related Topics
Related Topics

 Related Topics
Related Topics