The failover process, including script processing, can be tested at any time. To force unavailability, disconnect the network cable from a monitored machine, wait for the Time to Fail counter to decrease to zero and failover begins. To avoid the countdown delay, highlight the monitored machine name in the Failover Control Center window and select Failover.
Note: If the target is a cluster, you must click Failover from the active node of the target cluster. After failover is complete, click Failover on the passive node(s). This ensures that all nodes of the target cluster are aware of the failover so the source cannot overwrite the target's data on any of the node(s) of the target cluster.
If Manual Intervention is enabled, the Failover Control Center will prompt you when a failure occurs. Click Cancel to abort the failover process. (If necessary, you can initiate failover later from the Failover Control Center.) Click OK to proceed with failover.
Note: If the Failover Control Center is not running at the time the failure occurs, the manual intervention dialog box will appear the next time the Failover Control Center is started.
When a failure occurs, an alert is forwarded to the Windows event log. You can then start the Failover Control Center and respond to the manual intervention prompt.
If SNMP is installed and configured, an SNMP trap is also generated. When using a third-party SNMP manager, an e-mail or page can be generated to notify you of the failure.
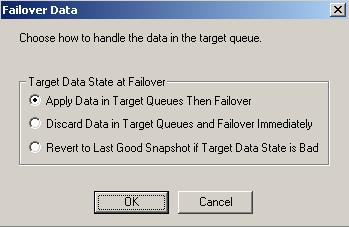
You will be prompted to specify what data you want to use on the target.

Select an option based on the table below. You may want to check the amount of data in queue on the target by reviewing the Statistics or Performance Monitor.
Apply Data in Target Queues Then Failover
All of the data in the target queue will be applied before failover begins.
Advantages—All of the data that the target has received will be applied before failover begins.
Disadvantages—Depending on the amount of data in queue, the amount of time to apply all of the data could be lengthy.
Discard Data in Target Queues and Failover Immediately
All of the data in the target queue will be discarded and failover will begin immediately.
Advantages—Failover will occur immediately.
Disadvantages—Any data in the target queue will be lost.
Revert to Last Good Snapshot if Target Data State is Bad
If the target data is in a bad Double-Take Availability state, Double-Take Availability will automatically revert to the last good Double-Take Availability snapshot before failover begins. If the target data is in a good state, Double-Take Availability will not revert the target data. Instead, Double-Take Availability will apply the data in the target queue and then failover.
Advantages—Good data on the target is guaranteed to be used.
Disadvantages—If the target data state is bad, you will lose any data between the last good snapshot and the failure.
After failover is complete, clients will be rerouted to the target, which is standing in for the source.
Exchange Note: Users using Outlook or Outlook Web Access to receive e-mail can connect after the changes have propagated through your environment. Users that had Outlook open during failover will need to restart the Outlook client (excluding Outlook Web Access clients on a LAN). Additionally, those users using Outlook Web Access or Outlook 2007 may see a security alert because the security certificate has the source server name but Exchange is now on the target. Click Allow or OK to dismiss the alert.
You will not be able to log in to the domain from the source Exchange server after failover because the target has assumed the source server's host Service Principal Name so that Outlook Web Access can use the source name. If you need to log in to the domain and Outlook Web Access is not needed, contact technical support for a workaround.
If you SMTP gateway is configured to send e-mail to a specific IP address that address is not failed over to the target, you will need to update the IP address after failover.
Mail stores or storage groups created after a failover will not be failed back.
SQL Note: After failover, linked databases in the SQL instance will be unavailable until the service master key is updated. You will need to run the command "alter service master key force regenerate" against the SQL target server to reset the service master key and then remove and re-add the linked servers into the target SQL instance.
After failover with a snapshot of a SQL database-only server, the SQL services on the target server are stopped and the databases are not mounted. You will need to manually start the MSSQLServer service for each instance on the target server and then manually attach the databases.
After failing over SQL 2008, Rich Internet Applications created using ADO.net 2 may not connect.
After failing over SQL 2008, you may not be able to take the SQL database offline. If this occurs, stop and restart the SQL Server Management Studio application, and then you can take the database offline.
After failing over in a SQL workgroup, you will not be able to connect to the source server instance of SQL. You can work around this issue by creating an alias on the target with the source server’s name.
BlackBerry Note: There is a potential to lose BlackBerry instant messages and instant message contacts when an Exchange mailbox is moved, depending on the type of BlackBerry hand-held device. You should back up instant messages through the BlackBerry desktop software or have the BlackBerry Enterprise server configured to audit all instant messages through a policy.