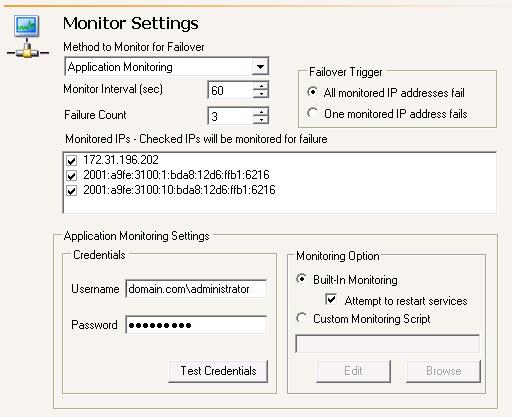

| Note: |
To achieve shorter delays before failover, use lower Monitor Interval and Failure Count values. This may be necessary for IP addresses on servers that must remain available and responsive at all times. Lower values should be used where redundant interfaces and high-speed, reliable network links are available to prevent the false detection of failure. If the hardware does not support reliable communications, lower values can lead to premature failover. To achieve longer delays before failover, choose higher values. This may be necessary for IP addresses on slower networks or on a server that is not transaction critical. For example, failover would not be necessary in the case of a server restart. Additionally, in a cluster environment, you must take into account the time it will take for a virtual server to failover between nodes. |
| Note: |
A sample Visual Basic script for application monitoring is available in the \Application Manager\Samples subdirectory where Double-Take Availability is installed. If you are using a PowerShell script, PowerShell must be installed on the target. |