

|
Use these instructions to restore your data first and then failback.
Review the Welcome screen and click Next to continue.
At any time while using the Restoration Wizard, click Back to return to previous screens and review your selections.
Select your network route to the new source, which includes the IP address and port number. Also select the location on the new source for the restored data. If you want to set a customized path, click in the field under Source Path to edit the location.

Specify the restoration options that you want to use.
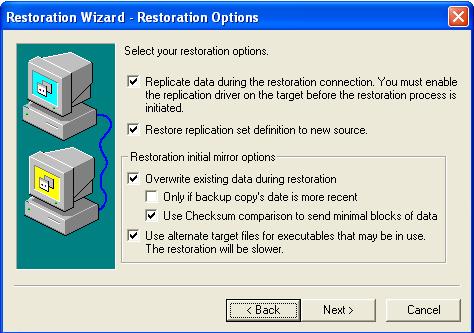
Overwrite existing data during restore—This option restores all existing files by overwriting them and writes any files that do not exist. If this option is disabled, only files that do not exist on the new source will be restored.
Only if backup copy's date is more recent—This option restores only those files that are newer on the target than on the new source. The entire file is overwritten with this option.
If you are using a database application, do not use the newer option unless you know for certain you need it. With database applications, it is critical that all files, not just some of them that might be newer, get restored.
To ensure data integrity, the replicate during restoration and overwrite existing data options are dependent on each other. If you want to enable replication, overwrite data will automatically be enabled. If you disable the option to overwrite data, replication will automatically be disabled.
At this time, you can go back to the dialog box in the Failover Control Center. Select Continue or Stop to indicate if you want to continue monitoring the source. After you have selected whether or not to continue monitoring the source, the source post-failback script, if configured, will be started.
The source must be online and Double-Take Availability must be running to ensure that the source post-failback script can be started. If the source has not completed its boot process, the command to start the script may be lost and the script will not be initiated.
At this time, you can start any applications and allow end-users to access the data.